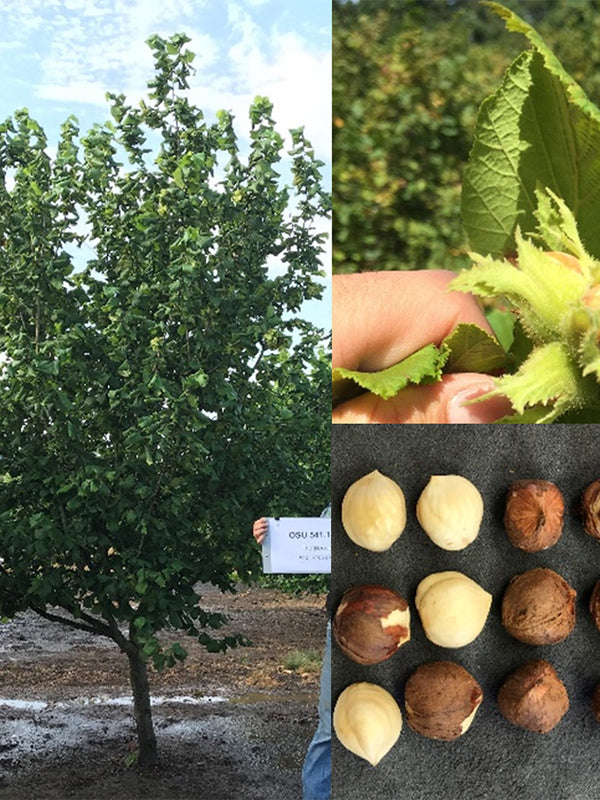
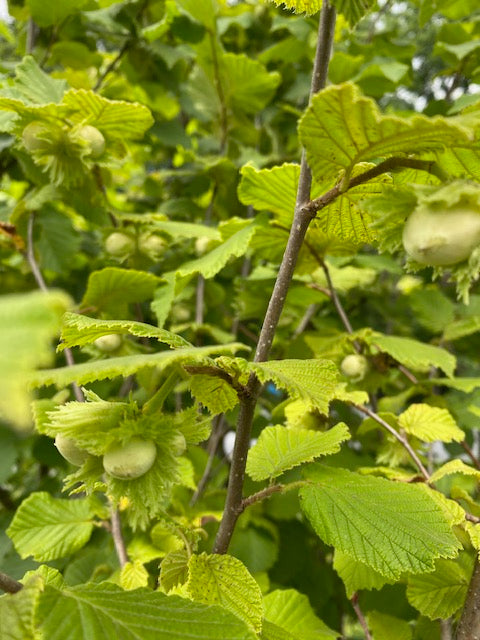
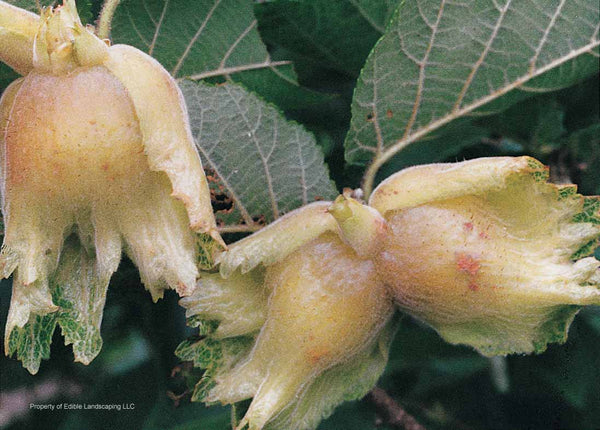
Corylus americana
A pretty hedge bush 6-8 feet tall. Native to the eastern U.S. Two plants are needed to set fruit. Very showy catkins in spring. Sweet small nuts ripen in August. Space 6' circle. Zones 5-8.
| Plant Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Pest Resistance | Excellent |
| Disease Resistance | Very Good |
| Drought Tolerance | Good |
| Heat Tolerance | Good |
| Humidity Tolerance | Good |
| Sun Tolerance | Good |
| Wet Soil Tolerance | Fair |
| Shade Tolerance | Fair |
| No Spray | Very Good |
| Salt Tolerance | Poor |
| Fresh for Kids | Good |
| Deer Resistance | Fair |
| Thorns | No |
| Plant Type | Shrub |
| Soil Type | Adaptable |
| Edible Type | Nut |
| Self Fertile | No |
| This information is accurate to the best of our knowledge, comments/opinions are always welcome | |
Due to import restrictions we are unable to ship Native American Filbert to Europe,...

Filbert in the winter
Filberts also called hazelnuts or hazels, filberts are deciduous shrubs 6' to 30' which produce small nuts in the fall. They grow best in zones 8 and 9 in the Northwest, but to well in 6 and 7 pretty much throughout the country. Self-unfruitful; plant at least two varieties.
Culture
Plant filberts in a spot protected from bitter winter winds. The plants do not have tap roots, but put down very deep roots. They should have a deep, well drained, fertile, humus soil. In colder climates, where plants don't grow as large they need a space only 10 to 12' across.
Because filberts are small trees, it is more practical to mulch then than larger nut trees. Use hay, leaves, or other organic material. The nutrients the mulch contributes to the soil is important to maintain of vigorous growth and good nut production. Further to promote growth, you should fertilize the plants with a balanced fertilizer such as 20-10-10. Apply 1/2 cup after the young plants are making growth; 1 cup the next year; and from then on increase the dosage by 1 cup a year until you reach 6. This is about the maximum for cold climates; but in milder areas, you can increase the supply 30 to 50%.
Filberts start to bear two or three years after they are planted. They reach good production three or four years later, but are likely to become erratic after ten years unless they are pruned severely.
Nuts are harvested from the ground after they drop. If the husks remain, these must be removed. The nuts should then be spread out in a warm dry, shady place to dry.